Glossary | Common Terminology for Public Speaking, Presentation, & Communication Skills
Public Speaking Glossary:
Audience: The group of people who will be listening to the speaker’s presentation.
Body language: The nonverbal communication that conveys the speaker’s emotions, attitude, and confidence.
Delivery: The way the speaker delivers their speech, including the tone, pace, and inflection.
Eye contact: Making direct eye contact with members of the audience to establish a connection and convey confidence.
Feedback: Response or reaction from the audience after the speaker’s presentation.
Gesture: A physical movement of the speaker’s body that communicates emphasis or emotion.
Memorization: Learning and delivering a speech from memory.
Outline: A brief summary of the speech’s main points and supporting evidence.
Vocal variety: The way the speaker uses their voice to convey meaning and emotion.
Non-verbal communication: using the bodily features (from gestures to facial contortions) to convey messages
High power poses: gestures or postures that increase the surface area that a speaker occupies with his/ her body; said to aid the boost in feel-good hormones in one’s body, thus amplifies one’s speaking confidence
Low power poses: closed-up postures or stances (smaller surface area being occupied), making speaker feel and look tentative
High-stakes presentation: make or break, “do-or-die” presentations; presentations that are linked to substantial commercial benefits or personal/ career advancements
Fleeting/ Panning eye contact: most of the time, such eye contact either portray tentativeness/ anxiety and shyness, or gives off the impression that the speaker is only patronizing the audience by panning the eye contact about (doing for the sake of doing it)
Sustained eye contact: intentional and strategic as it conveys genuine interest in driving home a point to a particular audience member
Ethos: refers to a speaker’s credibility, whether the audience sees him/ her as a subject matter expert and confers significance and recognition to what he/ she has to say
Pathos: refers to the emotional investment that a speaker has placed in his/ her speech, thus able to connect with his/ her audience at the psychological/ emotional level
Logos: refers to the logical flow of the speech/ the speaker’s speech content, whether it is coherent and based on logic and facts instead of hearsay and falsehoods
Internalization/ internalize: this is different from memorize/ memorization, it means that stage where a speaker is able to deeply understand the crux of the content and will be able to ditch a verbatim regurgitation of the script/ content during the presentation; instead, able to coherently put across the substantive and pivotal pieces of information even though it may differ slightly from the script
Hand gestures: Gestures are a form of nonverbal communication in which visible bodily actions are used to communicate important messages. For example, numbering gesture, palm-in-air (open) gesture, circular gesture, finger-pointing gesture
Stage positioning: Stage positions are used to help keep track of how performers and set pieces move during rehearsal and performance
Eye contact: the state in which two people are aware of looking directly into one another’s eyes.
Bridging: using a smile (to build rapport with audience) to bridge the distance between you and your audience, bring their barriers down
Pace: verbal speech at a particular rate or speed; for example, 2-3 words/ sec (moderate pace formula)
Rehearse: to practise a play, a piece of music, etc. in order to prepare it for public performance
Vocal projection: Voice projection is the strength of speaking or singing whereby the human voice is used powerfully and clearly.
Body language leakage (example – swaying left to right) – the accidental admission or escape of nervous cues
Pause fillers: a filler word is an apparently meaningless word, phrase, or sound that marks a pause or hesitation in speech (example – ‘erm’, ‘actually’, ‘you know…’)
Audience interaction: ask questions to engage audience, post a survey – ‘show of hands, how many of you…’, elicit a response and speak on that
Acronyms: an abbreviation formed from the initial letters of other words and pronounced as a word, so as to make it memorable and receptive to the audience (e.g. the “A.C.E” method to lose weight)
Quotations: a group of words taken from a text or speech and repeated by someone other than the original author or speaker.
Pause (for impact): a deliberate, temporary stop in action or speech to refocus attention of the speaker
Presentation Skills Glossary:

Timing: The ability to manage the length of a presentation, ensuring that it fits within the allotted time frame.
Organisational flow: The structure and flow of a presentation, including the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Persuasion: The act of convincing the audience to adopt a particular point of view or take action.
Engagement: The ability to capture and maintain the audience’s attention and interest throughout the presentation.
Preparation: The process of researching, organizing, and practicing a presentation prior to delivery.
Powerpoint Presentation slides: A PowerPoint presentation slide is similar to a poster presentation, only the information is on computer slides rather than actual posters. They are usually used to accompany an oral presentation
Adaptability: The ability to adjust and modify the presentation based on audience feedback or unexpected circumstances.
Storytelling: Using narrative techniques to engage the audience and communicate a message.
Clarity: The ability to communicate ideas and information clearly and effectively.
Rehearsal: Practicing the presentation in advance to ensure fluency and confidence.
Communication Glossary:

Verbal communication: The use of spoken or written words to convey a message.
Non-verbal communication: Communication without words, such as body language or facial expressions.
Interpersonal communication: Communication between two or more people (Interpersonal communication tips)
Constructive Feedback: The meaningful and beneficial response or reaction to a message or communication.
Perception: The way individuals interpret and understand the message.
Tone: The attitude or emotion conveyed through the speaker’s voice or written message.
Active listening: The act of actively engaging with the speaker and demonstrating understanding.
Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of another person.
Communication barriers: Anything that impedes effective communication, such as language barriers, physical barriers, or distractions.
Speech Glossary:

Oratory – the art of public speaking (road to 2016 World Champion)
Rhetoric – the use of language to persuade or influence
Address – a formal speech given on a particular occasion
Keynote – the main speech given at an event
Monologue – a long speech given by one person
Eulogy – a speech given at a funeral or memorial service
Commencement – a speech given at a graduation ceremony
Debate Glossary:

Argument – a statement put forward to support or oppose a claim
Proposition – a statement or idea that is being debated
Rebuttal – an argument that opposes or refutes a previous statement
Cross-examination – a questioning process in a debate or trial
Moderator – the person who leads or oversees a debate
Point of Order/ information – a procedural request or objection made during a debate
Adjudication – the process of deciding a winner or outcome of a debate
Persuasion Glossary:
Influence – the ability to change someone’s mind or behavior
Appeal – a persuasive message designed to evoke a particular emotion or response
Credibility – the believability or trustworthiness of a source or message
Call-to-action – a request or demand for the audience to take a specific action
Propaganda – information that is spread to promote a particular viewpoint or agenda
Manipulation – the use of deceptive tactics to influence or control someone
Negotiation – a process of discussion and compromise to reach an agreement or resolution
Interpersonal Conversation Glossary:

Dialogue – a conversation between two or more people
Active listening – the process of fully engaging and responding to what someone is saying
Paraphrasing – restating what someone said in your own words to show understanding
Non-verbal communication – communication through body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice
‘Feel the room/ vibe’ – being aware of someone’s communication that provides information on how they are coming across
Empathy – the ability to understand and share someone else’s feelings
Conflict resolution – the process of resolving disagreements or differences in a conversation or relationship
Small Talk Glossary:
Chit-chat – informal conversation about non-serious topics
Icebreaker – a topic or question used to initiate a conversation
Small talk etiquette – rules or norms that govern how small talk is conducted
Filler – a phrase or word used to avoid silence or awkwardness in conversation
Common ground – shared interests or experiences that form the basis of small talk
Open-ended question – a question that requires more than a yes or no answer
Banter – playful and humorous conversation between two or more people
Storytelling Glossary:
Narrative – a spoken or written account of events or experiences
Plot – the sequence of events in a story
Character – a person or animal that appears in a story
Setting – the time and place in which a story takes place
Conflict – a struggle or problem that a character must overcome
Climax – the turning point or highest point of tension in a story
Resolution – the outcome or ending of a story
Speech Craft/ Script Writing Glossary:
Dialogue – the spoken lines between characters in a script
Action – descriptions of physical actions or movements in a script
Character description – details about a character’s appearance, personality, and background
Scene – a specific location or setting in a script (using any of the five senses to ‘set the scene’)
Plot – the sequence of events that make up the story in a script
Screenplay – a script specifically written for a film or television show
Stage directions – instructions for actors and directors on how to perform a scene in a script
Story Curve Glossary:
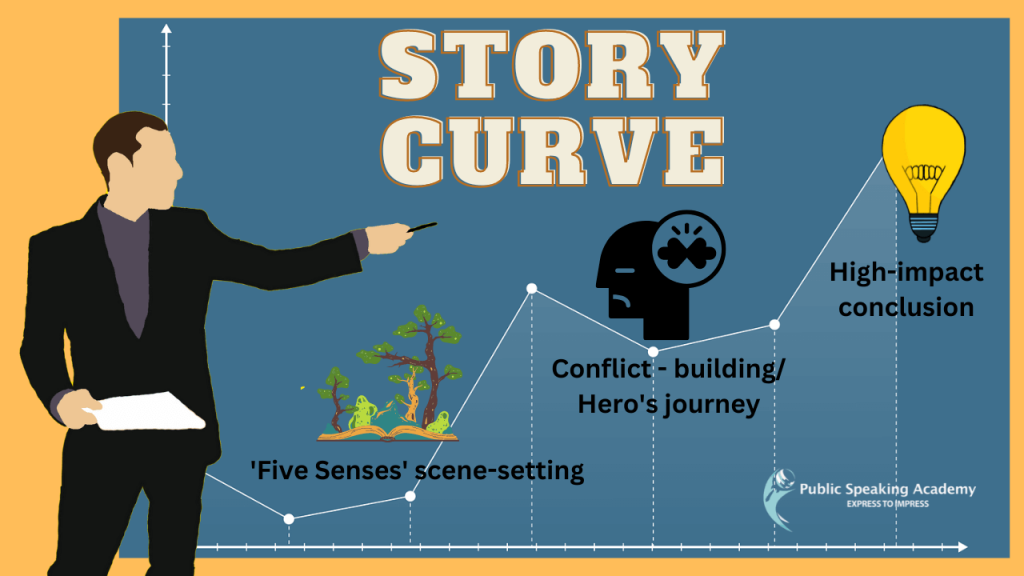
Exposition – the beginning of a story where the setting, characters, and conflict are introduced
Rising Action / Building the tension – the series of events that build tension and lead to the climax of the story
Climax – the turning point or moment of highest tension in a story
Falling Action – the events that occur after the climax, leading to the resolution of the story
Resolution / Conclusion – the end of the story where the conflict is resolved and loose ends are tied up/ / laying out the learning point, moral of the story
Plot – the sequence of events that make up a story
Narration – the act of telling a story
Oration Glossary:
Delivery – the manner in which a speech or oration is given
Intonation – the rise and fall of pitch and tone in speech
Articulation – the clarity and pronunciation of words in speech
Inflection – the change in pitch or tone to convey meaning or emotion
Gesticulate – the physical movements or expressions used to emphasize or convey meaning in speech
Diction – the choice and use of words in speech
Pace – the speed at which a speech is delivered
Hosting / Emceeing / Compere Glossary:

Master of Ceremonies (MC) – the person who hosts and leads an event or ceremony
Hospitality – the friendly and welcoming treatment of guests or attendees
Etiquette – the rules and customs governing behavior in a social setting
Protocol – the prescribed order or sequence of events in a formal setting
Agenda – the schedule or plan for an event or meeting
Warm-up – the introductory remarks or activities used to set the tone and engage the audience
Closing remarks – the final comments made by the host to wrap up an event
Introductory Remarks – the initial comments made by the emcee to introduce the event or speakers
Stage Presence – the way in which the emcee presents themselves on stage
Ad-Lib – the ability to improvise or speak spontaneously without a script
Crowd Control – the ability to manage and direct the audience during an event
Timing – the ability to keep the event running on schedule and to pace the program appropriately
Transitions – the smooth and seamless movement between different parts of the event
Intermission – the break or pause in an event for refreshments, rest or other activities
Impromptu Speaking Glossary:
Extemporaneous speaking – speaking without preparation or notes
Spontaneity – the quality of being impulsive or spontaneous in speech
Quick-wittedness – the ability to think and respond quickly
On-the-spot – a situation that requires an immediate response or improvisation
Think on your feet – the ability to improvise and come up with ideas quickly
Off-the-cuff speech – a speech given without preparation or advance notice
Charisma Glossary:
Charm – the ability to attract or influence others with one’s personality or character
Magnetism – the quality of being attractive or captivating
Presence – the quality of being engaging or compelling in person
Enthusiasm – intense and passionate interest or excitement
Charismatic communication – communication that is engaging, persuasive, and inspiring
Audience Engagement Glossary:

Interaction – the act of engaging with the audience, often through questions or discussion
Participation – the involvement of the audience in the speech or presentation
Call-to-action – a request or demand for the audience to take a specific action
Storytelling – the use of narrative to engage and connect with the audience
Visual aids – graphics, images, or videos used to enhance the audience’s understanding and engagement
Humor – the use of comedy or wit to engage and entertain the audience
Personalization / Tailored – customising the speech or presentation to the specific audience to increase engagement
Rapport-building Glossary:
Connection – a feeling of understanding or connection between two or more people
Trust – the belief that someone is reliable, honest, and sincere
Bonding – the act of creating a close relationship or connection with someone
Empathy – the ability to understand and share someone else’s feelings
Mutual respect – the recognition of each other’s worth and value
Communication – the exchange of information and ideas between two or more people
Building rapport – the process of establishing a relationship or connection with someone, often through shared interests or experiences.
Oral Assessment Glossary:
Oral exam – a test where a student is required to speak and answer questions verbally
Stimulus-based conversation – the stimulus based oral (SBO)conversation at the PSLE Oral Examination requires your child to have a conversation with the examiner, using the picture (stimulus) as a conversation starter.
Reading aloud – reading aloud is an instructional practice where the reader incorporates variations in pitch, tone, pace, volume, pauses, eye contact, questions, and comments to produce a fluent and enjoyable delivery of a text
Spoken interaction (for Cambridge O-level English) – Spoken interaction assessment refers to the testing of a student’s ability to actually hold, maintain and continue a conversation.
Oral interpretation – the performance of literature through spoken word
Speech evaluation – the process of assessing and providing feedback on a speaker’s performance
Theatre Performance / Speech and Drama Glossary:
Acting – the profession of performing in plays, movies, or television
Stage directions – instructions given in a script for how actors should move or speak
Blocking – the arrangement and movement of actors on stage
Set design – the creation and arrangement of scenery, props, and backdrops for a play
Dress rehearsal – the final practice run of a play with costumes and props
Monologue – a long speech given by one character in a play or performance
Script analysis – the process of analyzing and interpreting a play script to inform performance choices
Interview Glossary:

Job interview – a formal meeting between an employer and a potential employee to discuss a job opportunity
Informational interview – a meeting with a professional in a field to gain insights and information about a career or industry
Behavioral interview – an interview technique where the interviewer asks about past behaviors to predict future performance
Panel / Group interview – an interview where the candidate is interviewed by a group of people / or a multiple candidates interviewed by one or more assessors at the same time
Technical interview – an interview where the candidate is asked technical questions to assess their skills and knowledge
Case interview – an interview where the candidate is given a hypothetical problem to solve
DSA interview – Direct School Admission is a scheme in Singapore introduced in 2004 for students who are entering secondary school or junior college. The scheme allows education institutions to select and enroll students based on both their academic and non-academic talents and achievements instead of purely academic results. The interview is crucial in securing a seat via DSA.
Sales Pitch Glossary:

Sales presentation / pitch – a persuasive message designed to sell a product or service
Sales script – a written or memorized guide for delivering a sales pitch
Features – the specific characteristics of a product or service
Benefits – the advantages or positive outcomes that a product or service provides
Unique selling proposition (USP) – a factor that sets a product or service apart from competitors
Call-to-action – a request or demand for the listener to take a specific action
Objection handling – the process of addressing and overcoming potential customer concerns or questions
Elevator Pitch Glossary:
Briefing – a short verbal presentation designed to provide a concise overview of a product or service
Concise – clear and to the point, without unnecessary detail or elaboration
Value proposition – a clear statement of the unique value that a product or service provides
Differentiation – a factor that sets a product or service apart from competitors
Memorable – easy to remember and recall after a brief encounter
Tailored – customized to the specific needs and interests of the listener
Hook – a catchy or intriguing opening statement that captures the listener’s attention
Stage Fright Glossary:

Stage anxiety: The fear or apprehension associated with performing in front of an audience.
Glossophobia: The fear of public speaking or performing. (How to conquer stage fright?)
Nervousness: A state of being anxious or worried, especially about something important or uncertain.
Panic Attack: A sudden onset of intense fear or discomfort that often includes physical symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shortness of breath.
Freezing: A feeling of being unable to move or speak due to extreme nervousness or anxiety.
Self-Doubt: A lack of confidence in one’s abilities or self-worth.
Perfectionism: The desire to perform flawlessly or to meet an ideal standard, which can lead to excessive stress and anxiety.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: The idea that a person’s expectations or beliefs about themselves can become true simply because they believe them to be true.
Rehearsal: A practice session for a performance or presentation, often used to alleviate stage fright.
Coping Strategies / mechanism: Techniques or methods used to manage or reduce feelings of anxiety, such as deep breathing or positive self-talk.
Social Anxiety: A type of anxiety disorder characterized by intense fear or anxiety in social situations.
Phobia: An intense fear or aversion to a specific object or situation, such as heights, spiders, or flying.
Catastrophic Thinking: A type of negative thinking in which a person imagines the worst-case scenario in a situation, often leading to increased anxiety and stress.
Mindfulness: a state of active, open attention to the present moment, characterized by curiosity, acceptance, and non-judgment.
Stress: a physical or emotional response to a demanding situation, often leading to feelings of anxiety, tension, or overwhelm.
Reduction: the act of making something smaller or less intense.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR): a structured program designed to help individuals cultivate mindfulness skills as a way of reducing stress, anxiety, and other negative emotions.
Meditation: a practice of focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity, as a way of developing mindfulness and reducing stress.
Body scan: a guided meditation practice in which individuals focus their attention on different parts of the body, noticing physical sensations and learning to release tension.
Being mindful: a practice of moving the body with awareness and intention, paying attention to the sensations, both internal and external stimulations – having your mind on what you are doing/ feeling at the present. It’s the opposite of rushing or doing too many things at once.
If you want to learn more about delivering engaging, presentations and boosting your speaking confidence, check out our weekly public speaking & presentation skills course which covers all you need to know to craft and deliver powerful speeches.
We also hold a 2-day S’Peak Performance (SPP) adult public speaking programme which covers the following five modules:
Speaking Confidence Building Strategy
Effective Presentation Techniques
Impromptu Speaking / Think-fast-on-the-feet skills
Speech Delivery Techniques
Framing:
The way a speaker positions or contextualizes information to influence how the audience perceives it.
Micro-pausing:
Brief, intentional pauses between key phrases or sentences to allow content to sink in and enhance rhythm.
Triadic Structure (Rule of Three):
A rhetorical technique that uses a trio of ideas or elements for memorability and impact (e.g., “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”).
Anchor Statements:
Short, memorable phrases repeated or emphasized throughout a presentation to reinforce the message.
Stage Anchoring:
The practice of associating specific points or stories with physical positions on stage to aid memory and create spatial flow.
Voice Modulation:
Adjusting pitch, pace, volume, and tone for vocal expressiveness and clarity.
Energy Management:
The ability to regulate one’s physical and emotional energy levels throughout a speech for maximum impact.
🧠 Audience Psychology
Cognitive Load:
The mental effort required to process information; speakers must avoid overloading the audience with too much data.
Primacy Effect:
The tendency for audiences to better remember information presented at the beginning of a speech.
Recency Effect:
The tendency to recall the last part of a presentation more clearly than the middle.
Confirmation Bias:
The audience’s tendency to favor information that confirms their existing beliefs — speakers must acknowledge and strategically navigate this.
🧩 Content Strategy / Structure
Content Chunking:
Organizing content into digestible sections or “chunks” to make it easier for the audience to follow and retain.
Socratic Method:
Engaging the audience by asking thought-provoking questions that lead them to reflect or reach conclusions.
Callback:
Referencing an earlier point or joke later in the speech to build cohesion and payoff.
Signposting:
Using verbal cues (e.g., “firstly,” “let’s move on to,” “in conclusion”) to guide the audience through the structure of your speech.
🎤 Voice & Vocal Health
Resonance:
The richness and depth of one’s voice produced by vibration in the vocal tract.
Glottal Fry (Vocal Fry):
A low, creaky vocal register that can sometimes undermine perceived authority if overused.
Hydration Strategy:
Ensuring optimal voice performance through pre-presentation hydration and avoiding dehydrating substances like caffeine.
🌐 Cultural Awareness in Public Speaking
Cultural Sensitivity:
The awareness and respectful consideration of cultural differences in communication style, humor, and references.
Code-switching:
Adapting language, tone, or delivery depending on the audience’s background, expectations, or cultural context.
📣 Speechwriting & Storytelling Techniques
Emotive Language:
Words or phrases specifically chosen to evoke an emotional response.
Parallelism:
Using repeated grammatical structures for rhythm and emphasis (e.g., “I came, I saw, I conquered”).
Metaphorical Framing:
Using metaphors to help audiences conceptualize abstract ideas more vividly (e.g., “life is a journey”).
Art of Persuasion
- Cognitive Dissonance: The mental discomfort experienced when holding contradictory beliefs, often targeted in persuasive efforts.
- Scarcity Principle: A persuasion technique where something is portrayed as more desirable because it’s rare or limited.
- Social Proof: The tendency to align behavior with what others are doing—used to persuade by referencing popularity or widespread approval.
- Foot-in-the-Door Technique: Gaining compliance with a small request to increase the chances of agreement with a larger request later.
- Boomerang Effect: When a persuasive attempt results in the opposite of the intended effect.
- Framing Effect: The way information is presented can influence decision-making and opinions.
- Normative Influence: Persuasion based on a person’s desire to be liked or accepted by others.
Storytelling
- Narrative Arc: The structure of a story, typically involving exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
- Character Development: The process of creating a believable and dynamic character within a story.
- Plot Device: An element introduced into a story to advance the plot or create conflict.
- Foreshadowing: A storytelling technique where subtle clues hint at events to come.
- Flashback: A scene set in a time earlier than the main story.
- Theme: The underlying message or insight explored in a story.
- Point of View (POV): The perspective from which a story is told (first-person, third-person, etc.).
Emceeing (MC-ing)
- Segue: A smooth transition between segments of a program or event.
- Call-and-Response: An interactive technique used to engage audiences, often used in emceeing.
- Crowd Warm-up: The process of energizing and engaging the audience before a performance or speaker begins.
- Ad Lib: An improvised line or remark made during a live performance or event.
- Program Flow: The sequence and timing of elements in an event or ceremony.
- Housekeeping Announcements: Basic logistical information delivered to the audience (e.g., restrooms, exits, breaks).
- Tone Setting: Establishing the mood or emotional atmosphere for an event through delivery and presence.
Neuroscience of Communication
- Mirror Neurons: Brain cells that activate both when performing and observing an action—crucial for empathy and understanding.
- Amygdala Hijack: When emotional responses override rational thinking, often in stressful or high-stakes communication.
- Neuroplasticity: The brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, relevant to learning communication skills.
- Cognitive Load: The total amount of mental effort being used in working memory; impacts message retention.
- Prefrontal Cortex: The area of the brain associated with decision-making, impulse control, and social behavior.
- Dopaminergic Response: Dopamine-driven reactions that relate to motivation and reward in communication.
- Oxytocin Effect: A hormone associated with bonding and trust—triggered through effective storytelling or empathetic communication.
Humor
- Punchline: The final part of a joke, usually delivering the comedic twist.
- Timing: The pacing of delivery that affects the effectiveness of a humorous line or joke.
- Callback: A comedic reference to an earlier joke or moment, creating continuity and humor.
- Deadpan Delivery: A style of humor delivered with an emotionless, serious tone.
- Irony: Expressing meaning using language that normally signifies the opposite, often humorous or sarcastic.
- Hyperbole: Exaggerated statements used for comedic or rhetorical effect.
- Self-Deprecation: Humor that targets the speaker’s own flaws or misfortunes to appear relatable or humble.
Conflict Management
- De-escalation: Techniques aimed at reducing tension or aggression in a conflict situation.
- Active Listening: Fully concentrating and responding empathetically during a conflict to improve understanding.
- Mediation: A process where a neutral third party helps those in conflict find a resolution.
- Win-Win Solution: A conflict resolution outcome that satisfies the needs of all parties involved.
- Assertive Communication: Expressing one’s needs and opinions confidently without aggression.
- Trigger Words: Phrases or expressions that can provoke emotional reactions and escalate conflict.
- Reframing: Changing the way a situation is viewed or described to reduce hostility or defensiveness.
Visual Design for Presentations
- Slide Deck: A collection of slides used to support a spoken presentation.
- White Space: The empty space around elements in a design that improves readability and aesthetics.
- Visual Hierarchy: The arrangement of elements to indicate importance or guide the viewer’s attention.
- Contrast: The difference in color, size, or shape that makes elements stand out.
- Data Visualization: Graphical representations of data (e.g., charts, infographics) to make information easier to understand.
- Typography: The style and appearance of printed text, including font selection, size, and spacing.
- Consistency: Maintaining a cohesive style in visuals to improve clarity and professionalism.
🧠 Motivational Talk
- Intrinsic Motivation
Definition: Motivation driven by internal rewards like personal growth, passion, or values.
Example: A speaker encouraging self-fulfillment over external achievements. - Extrinsic Motivation
Definition: Motivation influenced by external rewards or consequences.
Example: Using prizes or recognition to boost audience action. - Call to Greatness
Definition: An appeal that inspires the audience to rise above mediocrity and pursue excellence.
Example: “You were not born to be average—you were born to lead.” - Empowerment Language
Definition: Words or phrases that instill confidence, agency, and self-belief.
Example: “You have everything it takes within you.” - Emotional Anchoring
Definition: Tying a desired action to a strong emotional trigger or story.
Example: Sharing a personal moment of failure followed by triumph to inspire resilience. - Hero’s Journey Framing
Definition: Structuring your persuasive message as a classic journey from struggle to victory.
Example: Casting the audience as heroes overcoming their own obstacles. - Future Pacing
Definition: Helping the audience imagine their success or transformation in the future.
Example: “Imagine a year from now, you’ve already achieved this…” - Pain–Pleasure Principle
Definition: Motivating by contrasting the pain of inaction with the pleasure of action.
Example: “Staying stuck will cost you years… but the joy of breaking free is priceless.” - Persuasive Reframing
Definition: Shifting perspective to turn limiting beliefs into opportunities.
Example: “Failure isn’t the opposite of success—it’s part of the journey.” - Identity Appeal
Definition: Persuading by aligning the message with how the audience sees themselves or who they want to become.
Example: “You’re the kind of person who doesn’t give up.” - Vision Casting
Definition: Painting a vivid and emotionally resonant picture of a desirable future.
Example: “Picture a world where every child has access to clean water…” - Affirmational Language
Definition: Repeated positive statements that affirm the audience’s potential.
Example: “You are capable. You are strong. You are ready.” - Persuasive Urgency
Definition: Creating a sense of immediacy to inspire quick action.
Example: “Now is your time. This opportunity won’t wait.” - Passion-Driven Persuasion
Definition: Letting genuine excitement and conviction become the main persuasive force.
Example: A speaker’s energetic storytelling making the audience want to act immediately.
💻 Digital Storytelling
- Multimedia Narrative
Definition: A story told using a combination of digital media—text, audio, video, and visuals.
Example: A short film combining voiceover, music, and animation to tell a brand’s origin. - Transmedia Storytelling
Definition: Telling a single story or story experience across multiple platforms and formats.
Example: A narrative that unfolds on social media, in a video series, and in a mobile app. - Interactive Narrative
Definition: A story format that allows audience participation or choice.
Example: Choose-your-own-adventure web stories. - Visual Hierarchy
Definition: The arrangement of elements to guide viewers through a visual story.
Example: Using bold headers, motion graphics, and color to lead the eye. - Story Arc in Digital Media
Definition: The traditional structure (setup, conflict, resolution) applied to online formats.
Example: A YouTube video that opens with a challenge, shows the struggle, and ends in victory. - Digital Ethos
Definition: Building credibility and trust through online presence and content.
Example: Testimonials, behind-the-scenes stories, and social proof on Instagram. - Microstory
Definition: A very short story told in a few seconds or lines—ideal for social media.
Example: A 15-second TikTok showing a transformation from doubt to confidence. - Cinematic Language
Definition: Using camera angles, editing, sound, and lighting to enhance storytelling.
Example: Slow zoom on a speaker’s face as they deliver an emotional message. - Narrative Voiceover
Definition: Spoken narration that adds context, emotion, or clarity to visual content.
Example: A voice telling the story over a montage of clips and images. - Social Storytelling
Definition: Stories crafted specifically for engagement and sharing on social platforms.
Example: Instagram Stories documenting a day-in-the-life with a message. - Visual Metaphor
Definition: Using symbolic imagery to reinforce story themes.
Example: A wilted flower in a video representing burnout. - Storyboarding
Definition: Planning digital stories in sequence using sketches or images.
Example: Creating panels that map out each scene of a YouTube short. - Viral Narrative Hooks
Definition: Engaging openings that grab attention and encourage viewers to watch or share.
Example: “You won’t believe what happened at this wedding…” - Cross-Platform Consistency
Definition: Maintaining a coherent story identity across digital touchpoints.
Example: Using the same characters, colors, and themes on TikTok, YouTube, and a website. - Audio Branding
Definition: Using consistent music, voice tone, and sound effects as part of your story identity.
Example: A motivational podcast with a signature intro tune and empowering tone.
Leadership Communication Glossary
- Vision Casting
Definition: The process of clearly articulating an inspiring future state to align and motivate team members.
Example: A CEO outlining a five-year innovation plan to energize employees. - Executive Presence
Definition: The ability to project confidence, credibility, and clarity under pressure, often seen as essential for leaders.
Example: A manager presenting to the board with poise and strategic insight. - Communication Alignment
Definition: Ensuring that messages across all levels of an organization are consistent with leadership’s vision and values.
Example: A leadership team synchronizing internal memos with the public brand message. - Authentic Leadership Voice
Definition: Speaking with integrity and congruence between values, words, and actions.
Example: A leader who admits mistakes openly and takes responsibility in front of the team. - Strategic Messaging
Definition: Crafting communication that drives specific organizational outcomes and supports strategic goals.
Example: A campaign promoting a culture of innovation during company restructuring. - Leadership Storytelling
Definition: Using personal or organizational stories to convey values, build culture, or inspire change.
Example: A leader recounting a pivotal failure that led to growth and resilience. - Directive Communication
Definition: Providing clear, actionable instructions, often used in urgent or high-stakes situations.
Example: A military officer issuing precise orders under time pressure. - Transformational Communication
Definition: Communication that seeks to inspire, empower, and elevate individuals or teams toward high performance.
Example: A coach delivering a moving halftime speech to revitalize team morale. - Empathetic Listening
Definition: A leadership skill involving active listening with an intention to understand emotions and perspectives.
Example: A leader spending time understanding an employee’s challenges before making decisions. - Change Communication
Definition: Specialized communication used to manage transitions, reduce uncertainty, and maintain morale during organizational change.
Example: A department head guiding staff through a merger with transparent Q&A sessions. - Stakeholder Messaging
Definition: Tailoring communication to address the interests, concerns, and expectations of various stakeholder groups.
Example: Crafting different messages for investors, employees, and customers about a product delay. - Two-Way Communication
Definition: Encouraging dialogue and feedback between leadership and team members to foster trust and co-creation.
Example: A CEO conducting monthly open forums for staff questions. - Communication Agility
Definition: The ability to adapt messaging style and delivery to different audiences, contexts, and challenges.
Example: Switching from motivational speaking to data-driven briefings depending on the audience. - Clarity Under Pressure
Definition: The capacity to remain calm and communicate clearly during crises or intense situations.
Example: A hospital director briefing staff during an emergency protocol activation. - Influence Without Authority
Definition: The art of persuading and mobilizing others without relying on formal power or hierarchy.
Example: A project manager motivating cross-functional teams to adopt a new workflow. - Vision-to-Action Communication
Definition: Translating abstract ideas into concrete plans and day-to-day behaviors.
Example: Explaining how a company’s mission statement applies to frontline customer service.
🏛️ Political Communication
Spin
The strategic presentation of information to influence public perception, often by emphasizing favorable details and minimizing negatives.
Talking Points
Pre-approved phrases or positions used consistently by a candidate or party to maintain message discipline across different media appearances.
Media Framing
The way news outlets shape narratives and influence how audiences interpret political events through selective emphasis, exclusion, and language choices.
Soundbite
A short, catchy excerpt from a speech or interview designed for repetition in news broadcasts and social media.
Echo Chamber
An environment (often online) where individuals are exposed only to viewpoints that reinforce their existing beliefs, leading to polarized communication.
Agenda Setting
The media’s ability to influence the importance placed on topics by deciding which issues to highlight and how prominently to feature them.
Political Branding
The crafting of a politician’s public persona, including values, image, tone, and messaging, to build recognition and trust among voters.
Crisis Communication
Strategic messaging deployed in response to political scandals, disasters, or backlash to control the narrative and protect reputational damage.
Rhetorical Framing
How political actors linguistically frame an issue to align with ideologies, e.g., calling welfare “a handout” vs. “a safety net.”
Town Hall Format
A style of political communication where candidates interact directly with citizens, often responding to unscripted questions to display authenticity and relatability.
Partisan Messaging
Communication that aligns strictly with the ideologies of a political party, often reinforcing in-group identity and loyalty.
Policy Narrative
A compelling story used to explain a political proposal, often integrating characters (heroes/villains), stakes, and consequences.
Surrogates
Prominent supporters or spokespeople who speak on behalf of a candidate or party to reinforce key messages across diverse media.
Polling Language
Carefully crafted question wording used in political polling to reduce bias and influence public opinion.
Intercultural Communication Glossary
Cultural Competence
The ability to understand, appreciate, and effectively navigate cultural differences in communication styles, values, and norms.
High-Context Communication
A communication style where much of the message is conveyed through context, nonverbal cues, and shared cultural knowledge (e.g., Japan, Arab cultures).
Low-Context Communication
A communication style that prioritizes explicit, direct verbal expression, common in cultures like the U.S., Germany, and Scandinavia.
Power Distance
The extent to which a culture accepts unequal distribution of power. High power distance cultures may expect formality and hierarchy in communication.
Face-Saving
Efforts made to preserve dignity, honor, and social harmony, particularly important in East Asian and collectivist cultures.
Code-Switching
The practice of alternating between languages or dialects depending on the social context or audience, often to build rapport or convey identity.
Cultural Filter
The internal lens through which individuals interpret messages based on their own cultural upbringing, leading to potential misunderstandings.
Cross-Cultural Miscommunication
Misunderstandings that occur due to differing norms, assumptions, or nonverbal signals between cultures.
Ethnocentrism
The belief that one’s own culture or communication style is superior, often leading to barriers in intercultural understanding.
Communication Accommodation
Adjusting one’s communication style to match that of another culture to foster connection or reduce conflict.
Intercultural Sensitivity
An awareness of cultural differences and a willingness to adapt communication accordingly to avoid offense or misinterpretation.
Global English (or World Englishes)
The various localized forms of English used worldwide, each with distinct accents, idioms, and rules, important in international communication.
Collectivist vs. Individualist Cultures
Cultural dimensions that shape whether communication emphasizes group harmony (collectivist) or self-expression and independence (individualist).
Stereotype Threat
The risk of confirming negative cultural stereotypes, which can impact one’s communication confidence and performance in intercultural settings.
Intercultural Empathy
The capacity to emotionally and cognitively relate to someone from a different culture, crucial for building trust and rapport.
Campaign Rhetoric
Stump Speech
A standardized speech candidates deliver at various campaign stops, crafted to resonate across multiple audiences and reinforce the core campaign message.
Rally Cry
A short, powerful phrase designed to energize supporters and unify them around a shared cause or candidate. Example: “Yes We Can.”
Populist Appeal
A rhetorical strategy that positions the speaker as a voice of the common people, often in opposition to elites, institutions, or the establishment.
Attack Ad
A form of campaign messaging that focuses on undermining an opponent, often through emotionally charged or negative portrayals.
Wedge Issue
A controversial topic used strategically to divide the opponent’s base or to attract undecided voters by highlighting polarized positions.
Contrast Ad
An advertisement or speech element that clearly distinguishes the candidate’s policies, values, or record from their opponent’s.
Political Slogan
A memorable and emotionally resonant phrase that encapsulates a candidate’s message, often used across speeches, merchandise, and media.
Mudslinging
The use of personal attacks, insults, or scandalous claims to discredit an opponent, often detracting from substantive policy debate.
Debate Zinger
A sharp, witty one-liner or retort delivered during a debate, intended to be memorable and media-friendly, often used to score points or destabilize an opponent.
Triangulation
A strategy where a candidate adopts positions from both ends of the political spectrum to appeal to moderates or to neutralize opposition.
Dog Whistle Politics
Coded language or phrasing that conveys a specific message to a particular demographic while remaining innocuous or ambiguous to the general public.
Voter Persona
A generalized, fictionalized profile representing a segment of the electorate, used to tailor messages and strategies to appeal to different audiences.
Framing Device
A rhetorical tool that shapes how an issue is presented and understood. For example, calling a policy “tax relief” instead of “tax cuts for the wealthy.”
Emotional Priming
The intentional use of emotionally charged language, imagery, or narratives to evoke a desired emotional response before delivering a core message.
Value Signaling
Subtle or overt references to widely shared values (such as freedom, faith, or family) that help build audience trust and moral alignment with the speaker.
Leave a Reply